The Gene Polymorphism Causing Accumulation of Uric Acid and Fatty Liver
Title:
Meta Description: The enzyme aldolase can lead to digestive complaints, fatty liver, and accumulation of uric acid. If you have a polymorphism on the gene responsible for aldolase, you should avoid fructose as much as possible. Fagron NutriGen™ can test for fructose intolerance.
Introduction
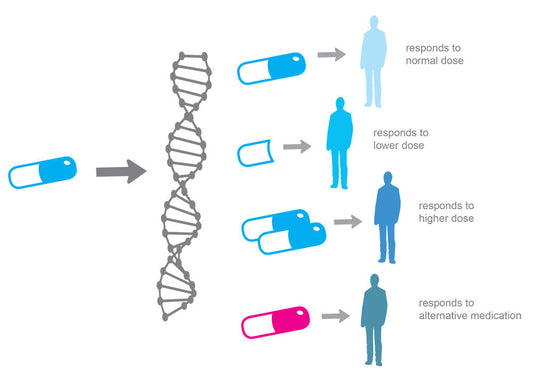
Our genes determine much of our body's physiology, including how we digest and metabolize different foods. One such gene is responsible for the enzyme aldolase, which plays a role in sugar metabolism. Some individuals have a polymorphism on this gene, leading to an accumulation of uric acid and fatty liver. Such individuals must avoid fructose as much as possible, as it can exacerbate these conditions. In this article, we explore the effects of aldolase polymorphism, fructose intolerance, and how to manage these conditions.
The enzyme aldolase causes an accumulation of uric acid, fatty liver and digestive complaints
Aldolase is an enzyme that plays a crucial role in sugar metabolism. It breaks down fructose-1,6-bisphosphate, a sugar molecule found in many foods, into two smaller sugar molecules. In individuals with a specific gene polymorphism, aldolase's activity can lead to the accumulation of uric acid, a waste product that can cause gout, and fatty liver. These conditions can cause digestive complaints such as bloating, constipation, and diarrhea.
If you have a polymorphism on the gene responsible for aldolase, avoid fructose as much as possible!
Individuals with an aldolase gene polymorphism must avoid fructose as much as possible. Fructose is found in many fruits, processed foods, and drinks, such as soda and sports drinks. Avoiding fructose can help manage uric acid and fatty liver accumulation. It is essential to read food labels carefully and avoid foods that contain high fructose corn syrup or fruit juice concentrates.
Fagron NutriGen™ also tests for fructose intolerance
Fructose intolerance is a condition where individuals have difficulty digesting fructose. It can cause similar symptoms as aldolase polymorphism, such as bloating, gas, and diarrhea. Fagron NutriGen™ can test for fructose intolerance and provide guidance on how much fructose an individual can tolerate. In some cases, individuals may only tolerate one piece of fruit a day.
Managing aldolase polymorphism and fructose intolerance
Managing aldolase polymorphism and fructose intolerance involves avoiding fructose as much as possible. Individuals can consume fruits that are lower in fructose, such as berries and citrus fruits, in moderation. Other tips include:
- Eating a diet rich in vegetables, lean proteins, and healthy fats.
- Drinking plenty of water and avoiding sugary drinks.
- Managing weight through regular exercise and a balanced diet.
- Seeking medical advice and treatment for gout and fatty liver.
FAQs
Q: What is aldolase? A: Aldolase is an enzyme that breaks down fructose-1,6-bisphosphate, a sugar molecule found in many foods.
Q: What is aldolase polymorphism? A: Aldolase polymorphism is a specific genetic variation that can lead to an accumulation of uric acid and fatty liver.
Q: What is fructose intolerance? A: Fructose intolerance is a condition where individuals have difficulty digesting fructose.
Q: Can individuals with aldolase polymorphism consume fruit? A: Individuals with aldolase polymorphism should limit their fructose intake, but they can consume fruits that are lower in fructose, such as berries and citrus fruits, in moderation.