Did You Know That Genetics and Lifestyle Play a Role in Type 2 Diabetes?
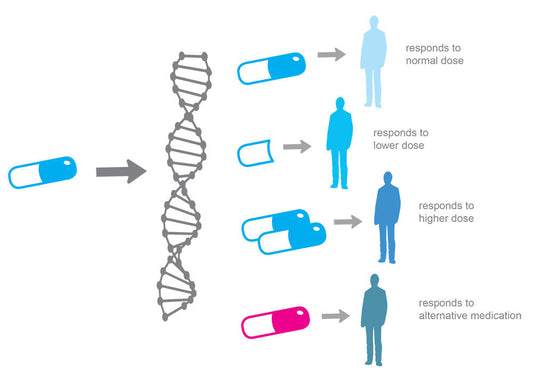
Did you know that both genetic predisposition and environmental factors play a role in the risk of type 2 diabetes mellitus? In fact, recent research has shown that genetics accounts for up to 70% of an individual's risk for developing type 2 diabetes, while lifestyle and environmental factors account for the remaining 30%.
At Fagron NutriGen™, we understand the importance of analyzing genetic predisposition to type 2 diabetes. Our advanced genetic testing technology analyzes 10 key genes that increase the risk of developing this disease, helping you to gain insight into your personal risk. By getting in touch with your healthcare professional and learning more about your genetic predisposition, you can develop a personalized plan to manage your risk and maintain your health.
Understanding the Role of Genetics in Type 2 Diabetes
Type 2 diabetes is a complex disease that arises from a combination of genetic, lifestyle, and environmental factors. While environmental factors such as diet and physical activity are widely recognized as contributing factors to the development of type 2 diabetes, genetic factors are often overlooked.
Recent research has shown that certain genetic variants increase an individual's risk for developing type 2 diabetes. These variants affect the way the body processes insulin, a hormone that regulates blood sugar levels. In some cases, genetic mutations can lead to insulin resistance, a condition in which the body becomes less responsive to insulin and blood sugar levels rise.
In addition to insulin resistance, genetic variants can also affect other aspects of metabolism, including the way the body processes fat and cholesterol. By analyzing these genetic variants, we can gain a better understanding of an individual's personal risk for developing type 2 diabetes and develop targeted interventions to manage that risk.
Lifestyle Interventions for Managing Type 2 Diabetes Risk
While genetics plays a significant role in the development of type 2 diabetes, lifestyle factors such as diet and exercise also play a critical role. In fact, research has shown that making lifestyle changes can significantly reduce an individual's risk of developing type 2 diabetes, even in those with a high genetic risk.
Maintaining a healthy body weight and waist circumference is key to managing type 2 diabetes risk. For individuals with a high risk of developing the disease, a low-calorie, very low-carb diet intervention may be the most effective strategy. Increasing intake of lean protein, probiotics, unsaturated fats, omega-3 fatty acids, and fiber can also be beneficial, while avoiding foods with refined carbohydrates and monitoring the glycemic index of foods can help regulate blood sugar levels.
Staying hydrated and avoiding alcohol consumption is also important, while regular exercise can positively impact glucose regulation. In some cases, supplementation with vitamins and minerals such as B1, B2, B6, nicotinamide, pantothenic acid, biotin, manganese, magnesium, and berberine may also be required to manage type 2 diabetes risk.
Conclusion
At Fagron NutriGen™, we understand the importance of analyzing genetic predisposition to type 2 diabetes. By analyzing 10 key genes that increase the risk of developing diabetes type 2.